The way we design digital products is shifting, fast. Where once we relied on static user journeys and generalized assumptions, today’s users expect more. They expect experiences that recognize their intent, adapt in real time, and reduce friction with every click.
This is where AI UX enters the equation.
Rather than designing one-size-fits-all interfaces, modern product teams are using artificial intelligence and behavioral analytics to shape digital experiences around each individual user. From personalized dashboards to adaptive navigation, the move toward AI-powered UX reflects a deeper need: context-aware design that evolves as user behavior changes.
It’s not about replacing designers with algorithms. Instead, it’s about amplifying what UX teams can do, making experiences more responsive, more intuitive, and far more aligned with what users actually want.
We’re already seeing this shift in tools we use daily. Think of how your feed updates on Netflix, or how Google surfaces content based on your habits. Behind the scenes, machine learning models analyze behavioral patterns, then tweak what’s shown, how it’s shown, and even when.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI and behavioral data combine to power personalized UX. We’ll break down the fundamentals of AI UX, how adaptive interfaces work, and what it takes to implement them responsibly, from data pipelines to ethical design. You’ll also see examples of real-world platforms that use UX strategy backed by AI to drive measurable results.
Because in today’s digital landscape, personalization is no longer a feature. It’s the foundation of modern UI/UX design.
What Is AI UX?
AI UX refers to the integration of artificial intelligence into the user experience design process, with the goal of delivering personalized, adaptive, and context-aware interfaces. It moves beyond traditional rules-based logic to create digital environments that respond dynamically to user behavior, without requiring manual intervention for every case.
At its core, AI-powered UX combines two key components:
1. Machine learning models trained on historical and real-time data
2. UX patterns that adapt based on predictions, preferences, or environmental triggers
The result is a user experience that continuously evolves, automatically.
Unlike standard personalization, which might display a user’s name or recommend a product based on a category, AI UX goes several steps further. It predicts next actions, adjusts layouts, and reorders content based on what each user is likely to find valuable at a given moment.
Example: Predictive Design in Action
Spotify doesn’t just suggest songs. It builds dynamically generated playlists, auto-adjusts home screen modules, and highlights recommendations based on time of day, listening habits, and user context. That’s not just personalization, it’s predictive, adaptive UX strategy at scale.
In practice, this means UI isn’t static. Interfaces can learn. They shift in response to signals like drop-off points, click hesitations, and repeated behaviors. Over time, the product becomes more aligned with how a user works, not just how it was designed.
As UI/UX design continues to evolve, AI UX is redefining the boundary between product and user. The interface becomes less of a barrier and more of a partner in task completion and discovery.
The Role of Behavioral Data in Personalization
Personalized experiences don’t happen in a vacuum, they’re powered by behavioral data. Every click, scroll, and pause tells a story about what users want, where they struggle, and what keeps them engaged. AI UX systems take that story and translate it into action.
Behavioral data refers to how users interact with your product over time. This includes:
- Click patterns and navigation paths
- Session length and frequency
- Feature usage depth
- Scroll behavior, form abandonment, and timing
While traditional UX relies heavily on upfront user research and personas, AI-powered UX uses actual behavior, at scale, to fine-tune design in real time. The more a user interacts with the product, the more the system learns, adapts, and personalizes accordingly.
Example: Amazon’s Homepage Adaptation
Amazon is a textbook case. The homepage layout changes based on browsing history, search behavior, and purchase patterns. Users who frequently browse electronics see more tech content. Those who shop for books are shown curated reading suggestions. The interface reshapes itself continuously, thanks to behavioral feedback loops.
This adaptive approach allows for micro-personalization. Rather than pushing every user through the same flow, UX strategy can be segmented based on real-time behavioral cohorts. One user might get tooltips for advanced features, while another sees a stripped-down interface that reduces complexity.
The role of behavioral data isn’t just reactive, it’s predictive. Over time, AI models begin to anticipate what users are likely to do next, helping designers surface the right content, in the right order, at the right time.
This is the real power behind AI UX: using live behavior, not assumptions, to design interfaces that feel personal, even at enterprise scale.
Designing Adaptive Interfaces with AI
Adaptive interfaces are where AI UX truly comes to life. Unlike static layouts built for one ideal user journey, adaptive interfaces shift in response to each user’s context, behavior, and preferences, often in real time.
These interfaces rely on backend intelligence, usually a combination of behavioral analytics, AI models, and UX rules, to make decisions about what the user sees or interacts with. The goal isn’t just to personalize; it’s to optimize the path to value for every individual.
Common Use Cases:
- Dynamic navigation menus that prioritize recently used or high-frequency features
- Contextual tooltips that appear based on user hesitation or repeated errors
- Content reordering to surface relevant modules based on previous behavior
- Real-time adjustments for screen layout based on user role or intent
Comparison Snapshot: Static vs. Adaptive UI
|
Feature |
Static Interface |
Adaptive Interface |
|
Navigation |
Same for all users |
Reprioritized per user behavior |
|
Onboarding |
Linear walkthrough |
Personalized, progressive prompts |
|
Content Sections |
Fixed placement |
Dynamic layout based on engagement data |
|
Updates |
Manual deployment |
Automated UI updates triggered by model input |
Well-executed AI-powered UX doesn’t feel intrusive, it feels invisible. The interface simply “gets” the user. That’s why leading digital platforms embed adaptive design into their core UX strategy, using data to serve the right interface at the right time.
Done right, adaptive design reduces friction, accelerates learning, and helps users complete tasks faster. It’s one of the clearest demonstrations of how AI UX elevates not just what a product does, but how it feels to use.
Balancing Personalization with UX Strategy
As powerful as AI-powered UX can be, more personalization isn’t always better. Too much adaptation, or the wrong kind, can disorient users, create inconsistency, or even erode trust. That’s why thoughtful UX strategy must guide how and where AI is applied.
Personalization should support clarity, not complicate it. For example, an adaptive interface that constantly reshuffles menu items might feel smart on paper but leave users hunting for familiar tools. The goal is to enhance usability, not replace predictability with surprise.
Strategic Principles to Keep in Mind:
1. Preserve core patterns. Adaptive elements should follow a consistent structure. Users still rely on anchors like navigation placement and labeling.
2. Avoid overfitting. Just because someone clicks one tab more than others doesn’t mean it should dominate the interface. Context matters.
3. Always offer control. Give users the ability to reset, opt out, or customize their experience. Transparency builds trust.
Platforms that get this balance right often use AI UX to subtly reinforce user intent, without taking full control. For instance, tools like Notion and Airtable may surface helpful templates or actions based on prior behavior, but they leave core structure untouched. That’s smart adaptation within limits.
To maintain long-term scalability, teams should monitor how personalization affects key metrics: time-on-task, error rates, drop-offs, and feature adoption. This ensures that AI-powered UX serves users without unintentionally introducing new friction.
In short, personalization isn’t just a design layer, it’s a decision-making system. And like any system, it needs boundaries. When grounded in strategy, AI UX becomes more than reactive, it becomes reliable.
Technical Implementation Framework
Behind every seamless AI-powered UX is a well-structured technical foundation. Personalization at scale requires more than good intentions, it demands the right architecture, tooling, and safeguards to deliver responsive, adaptive interfaces in real time.
So what does the typical implementation stack look like?
Core Components of an AI UX System:
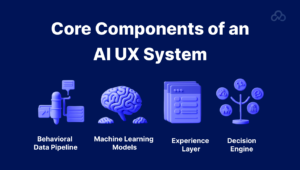
Behavioral Data Pipeline
Tracks and stores user events (clicks, scrolls, time-on-page, abandonment). Tools like Segment, Heap, or custom-built trackers handle this layer.
– Machine Learning Models
Predict next actions, personalize content, or adjust layouts. These models are trained on historical interaction data, using platforms like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or AWS SageMaker.
– Experience Layer / Front-End Integration
This is where predictions meet design. React, Vue, or Angular apps receive real-time data from APIs to re-render UI elements dynamically.
– Decision Engine
Coordinates what changes occur and when. Often rules-based systems (like LaunchDarkly) are combined with probabilistic models to refine UX without constant manual updates.
Don’t Forget Privacy
With all this data flowing behind the scenes, UX strategy must consider user trust. AI personalization can feel invasive if not handled responsibly.
Key considerations:
1. Anonymize behavioral data before training models
2. Ensure GDPR and CCPA compliance in all data capture systems
3. Provide opt-out mechanisms for personalized features
Measuring the Impact: Metrics That Matter
No matter how intelligent an interface is, its success hinges on one thing, results. To know whether your AI-powered UX efforts are working, you need clear, actionable metrics that reflect both user behavior and product outcomes.
The good news? AI UX generates rich behavioral data by default. The challenge is knowing what to measure, and why.
Key Metrics That Signal Effective AI UX
- Task Completion Rate
Are users able to finish key flows (e.g., setup, checkout, publishing) faster or more reliably?
- Time-to-Value
How long does it take a new user to reach their first meaningful result? AI-driven onboarding should shorten this.
- Feature Discovery Rate
Are users exploring the right features at the right time? Adaptive interfaces can surface tools that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Retention and Re-engagement
Has your churn rate improved? Are more users returning after day 1, day 7, or day 30? - Error Rate / Friction Points
Are personalized flows actually reducing user confusion, or introducing new barriers?
Example Table: Baseline vs. AI-Powered UX
|
Metric |
Before AI UX |
After AI UX |
|
Task Completion Rate |
72% |
88% |
|
Time-to-Value (avg) |
4.6 mins |
2.9 mins |
|
Feature Discovery Rate |
39% |
58% |
|
7-Day Retention |
23% |
35% |
Real-World Insight
Duolingo implemented an AI-powered UX to adjust difficulty levels dynamically. The result? Not only did daily active time increase by 14%, but dropout rates on difficult lessons dropped significantly, just by letting the interface adapt to user performance in real time.
Ultimately, measuring impact is about aligning your UX strategy with business goals. The right metrics don’t just tell you what’s happening, they help you decide what to improve next.
Challenges and Limitations
While the potential of AI-powered UX is significant, it’s far from a plug-and-play solution. Implementing adaptive interfaces introduces a new layer of complexity, one that requires careful consideration across design, engineering, ethics, and strategy.
Key Challenges to Watch For:
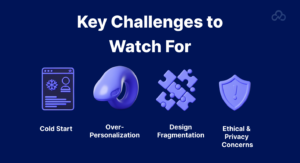
1. The Cold Start Problem
AI needs data to work. For new users or new products, personalization engines often struggle due to lack of behavioral history. Initial flows must be thoughtfully designed to perform well without AI input, gradually enhancing as data builds.
2. Over-Personalization
Too much personalization can backfire. When the interface changes too often or feels too opaque, users may lose confidence. This is especially risky in tools used by teams, where consistency matters across shared workspaces.
3. Design Fragmentation
Adapting UI for every behavior set can lead to inconsistent experiences. Teams need to enforce a UX strategy that defines boundaries, deciding which parts of the product should adapt and which should stay fixed.
4. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Behavioral tracking comes with legal and moral responsibility. Personalization that’s too aggressive, or worse, opaque, can feel invasive. Ensure users know what’s being personalized and why, and offer easy opt-outs.
Real Example:
A productivity app implemented location-based UI changes (e.g., adjusting interface settings based on region), but failed to inform users. After pushback, the team rolled out transparency prompts and saw trust and engagement bounce back.
The best AI UX implementations don’t just adapt, they respect the user. They’re designed with restraint, tested rigorously, and built around human oversight. When you balance flexibility with consistency, personalization becomes a competitive edge rather than a source of confusion.
Technical FAQs
Q1: What’s the difference between adaptive interfaces and responsive design?
Responsive design adjusts to screen size and device. Adaptive interfaces, powered by AI, adjust based on user behavior, preferences, and context. While both aim to improve usability, adaptive systems are dynamic and behavior-driven, not just layout-based.
Q2: How does AI determine what content or layout to show?
AI models analyze patterns in behavioral data, clicks, scrolls, feature usage, and even hesitation points. Based on this, the system predicts what a user is likely to need or prefer and adjusts the interface accordingly, often through predefined UI rules or ranking algorithms.
Q3: Can AI-powered UX work without large datasets?
Yes, to an extent. Rule-based personalization can function on limited data. However, for scalable, predictive AI UX, a certain threshold of behavioral history improves accuracy. Teams often start with hybrid systems, combining logic-based flows with machine learning that matures over time.
Q4: What are the privacy risks when using behavioral data in UX?
The main concerns involve transparency and consent. To stay compliant with GDPR, CCPA, and other frameworks, UX teams must anonymize sensitive data, explain how it’s used, and allow users to opt out. Clear communication is as essential as the personalization itself.
The Future of UX Is Smart, Not Static
The next generation of UX won’t be built on fixed screens and rigid flows. It’ll be built on systems that learn, quietly shaping themselves around each user’s context, goals, and habits. AI UX represents more than a trend. It’s a fundamental shift in how we design, test, and scale digital experiences.
But like any system built on automation, success depends on thoughtful constraints. The smartest interfaces aren’t the ones that change the most, they’re the ones that adapt when it matters, and stay familiar when it doesn’t.
For designers and product teams, the path forward isn’t just about implementing AI. It’s about building trust, maintaining usability, and aligning personalization with purpose. Done well, AI-powered UX becomes an engine for growth, clarity, and retention, without sacrificing control or consistency.
As more platforms adopt this approach, one thing becomes clear: in a world where every user expects relevance, UI/UX design that stays static will quickly fall behind.
The future of UX isn’t just intelligent. It’s responsive, respectful, and deeply human.
Do you like to read more educational content? Read our blogs at Cloudastra Technologies or contact us for business enquiry at Cloudastra Contact Us